Use the USB-camera and run opencv on racecar¶
In this section we bring up the USB-camera on the racecar and run opencv for simple application. We monitor the process by streaming the video to our local computer.
Setup and bring up the USB_cam¶
First sonnect to the car using ssh, with “-X” option, which enables graphics interface.
ssh -X tianbot@192.168.50.10*
Then simply running command:
roslaunch usb_cam usb_cam-test.launch
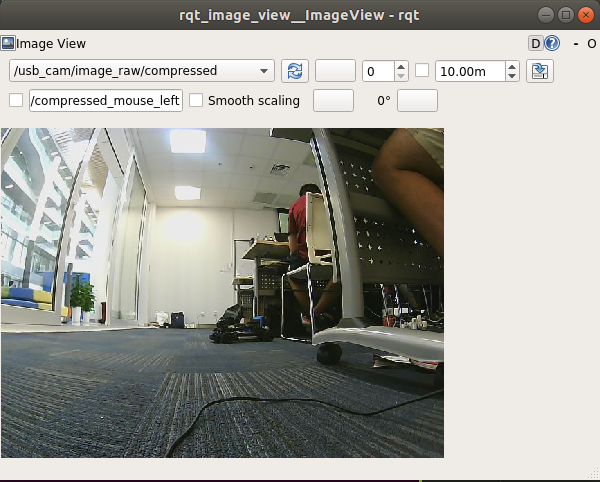
A window will pop up, select the menu on the top-left corner for /usb_cam/image_raw/compressed, then we should be able to see the video from the camera.
Running opencv¶
Opencv has already been installed on the Jetson Nano board on the racecar. To see it’s version, we simply test:
$ python
Python 2.7.15rc1 (default, Nov 12 2018, 14:31:15)
[GCC 7.3.0] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import cv2
>>> cv2.__version__
>>> '3.3.1'
Unfortunately, for opencv version 3.3.1, the MultiTracker class(see the last tutorial that we run on the local computer) has not been supported. Here we demonstrate simple image processing techniques as follows:
Open USB_cam in opencv¶
Here we demonstrate how to stream the USB_cam using opencv. Note that we don’t need to launch any node to read the camera signal. First create a python file “streaming.py”
gedit streaming.py
then copy and paste the following:
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
success, frame = cap.read()
cv2.imshow("streaming",frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == 27: # Esc pressed
break
Using Color filter¶
Here we demonstrate how to do simple color filtering.
First create another file called “filtering.py”
gedit filtering.py
Then copy and paste the following:
import numpy as np
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
def nothing(x):
pass
cv2.namedWindow('image',cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.resizeWindow('image',(600,200))
cv2.createTrackbar('minH', 'image', 0, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('minS', 'image', 0, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('minV', 'image', 0, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('maxH', 'image', 0, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('maxS', 'image', 0, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('maxV', 'image', 0, 255, nothing)
while True:
_, frame = cap.read()
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV) # convert to hsv encoding for better processing
minH = cv2.getTrackbarPos('minH', 'image')
minS = cv2.getTrackbarPos('minS', 'image')
minV = cv2.getTrackbarPos('minV', 'image')
maxH = cv2.getTrackbarPos('maxH', 'image')
maxS = cv2.getTrackbarPos('maxS', 'image')
maxV = cv2.getTrackbarPos('maxV', 'image')
a = cv2.waitKey(5) & 0xFF
if a == ord('p'):
print('minH: ', minH, '\nmaxH: ', maxH,'\nminS : ', minS, '\nmaxS : ', maxS\
,'\nminV : ',minV,'\nmaxV : ',maxV)
lowerpink = np.array([minH,minS,minV])
upperpink = np.array([maxH,maxS,maxV])
# print(lowerpink + '\n' + upperpink)
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv,lowerpink, upperpink)
res = cv2.bitwise_and(frame,frame, mask = mask)
# median = cv2.bilateralFilter(res,15,75,75)
# cv2.imshow('median',descale(median,3))
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
cv2.imshow('mask',mask)
cv2.imshow('res',res)
k = cv2.waitKey(5) & 0xFF
if k == 27:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cap.release()
You shuold be able to use the slider and select the color you want.
Edge detection¶
Here we demonstrate how to do simple edge detection.
First create another file called “edge.py”
gedit edge.py
Then copy and paste the following:
import cv2
import numpy as np
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
def nothing(x):
pass
cv2.namedWindow('image',cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.resizeWindow('image',(600,200))
cv2.createTrackbar('th1', 'image', 0, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('th2', 'image', 0, 255, nothing)
while True:
_, frame = cap.read()
th1 = cv2.getTrackbarPos('th1', 'image')
th2 = cv2.getTrackbarPos('th2', 'image')
laplacian = cv2.Laplacian(frame,cv2.CV_64F)
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(frame,cv2.CV_64F, 1, 0, ksize = 5)
sobely = cv2.Sobel(frame,cv2.CV_64F, 0, 1, ksize = 5)
edges = cv2.Canny(frame, th1, th2)
newedges = cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(newedges,127,255,0)
cv2.imshow('thresh', thresh)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(edges,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2:]
cv2.drawContours(frame,contours,-1,(0,0,255),1)
# print(len(contours))
# cv2.imshow('original',frame)
# cv2.imshow('laplacian',laplacian)
# cv2.imshow('sobelx',sobelx)
# cv2.imshow('sobely', sobely)
cv2.imshow('edges', edges)
cv2.imshow('frame', frame)
k = cv2.waitKey(5) & 0xFF
if k == 27:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cap.release()
You should be able to run the file and do simple edge detection.